Product introductionPea protein
Plant protein material extracted from pea

-
What is pea protein?
- It is a food material obtained by separating and refining protein contained in yellow pea (Pisum Sativum L.). It has features such as improving good emulsification effect and emulsification stability and product water retention, and contains a good balance of each amino acid and is excellent in nutritional value. It can be used for various processed foods as a new type of vegetable protein material not found in the past.
Main type

- Processed meat
- processed sausage, pressed ham,
Cooked ham, bacon

- Prepared foods
- Hamburgers, meatballs,
Dimsum, Tonkatsu

- Processed fish products
- Fish sausage,
Various surimi products

- Noodles
- Chinese noodles, udon, soba, pasta

- Confectionery
- cookies, donuts,
Snack confectionery, cereal food

- Bakery
- Bread and pastries
Sponge cake, muffin

- Seasonings
- Sauces, Dressings,
Mayonnaise, Sauce

- Other
- Batter mix, protein reinforced food,
Various frozen foods, others
Functions of pea protein
High solubility
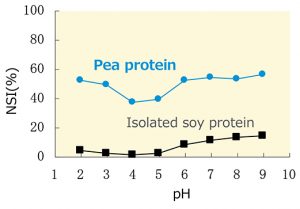
As with other protein, the pea protein shows relatively high solubility, although it decreases near the isoelectric point (pH 4.5 to 4.7). Also, even in the presence of sodium chloride, the decrease in the solubility of pea protein is slight, maintaining constant solubility in wide pH range.
-
- Water-soluble nitrogen index at each pH
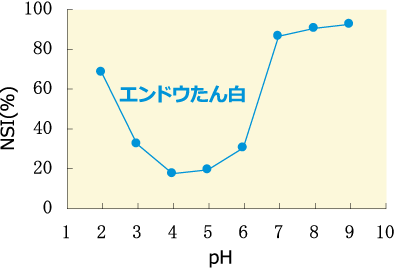
- * NSI (water-soluble nitrogen index): Percentage of water-soluble nitrogen relative to total nitrogen
-
- Water soluble nitrogen index in 2% salt solution
Stable emulsifying effect
Pea protein is a protein material excellent in emulsifying effect compared to soy protein. It is also excellent in emulsion stability, and the emulsion prepared using this has heat resistance and salt tolerance.
-
- Emulsion stability
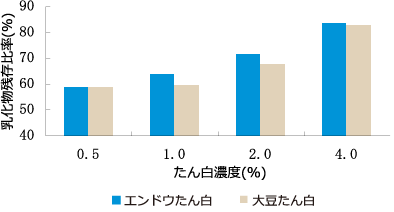
- The result of comparing the stability of the O / W type emulsion with the emulsifying effect-strengthened type soy protein. It shows the remaining ratio (%) of emulsion heated at 80 ° C for 1 hour and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes.
-
- Emulsion stability (in the presence of sodium chloride)
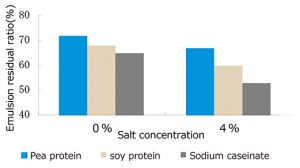
- This is the result of comparing salt tolerance of O / W type emulsion with soy protein, casein sodium. With two emulsfied products: one without added salt and the other with 4% added salt, it shows the remaining ratio (%) of the emulsion after processed under the same conditions as above.
Excellent water retention
Pea protein is a protein with excellent water retention. It is hard to be affected by sodium chloride, and it is strong in freezing and thawing processing. The right graph indicates, the gel of the dried white egg is denatured in a sponge-like shape under the freezing and thawing treatment, causing a large amount of dripping, but the gel of pea protein has almost no apparent change. Among the three types of protein compared, it is understood that pea protein is the most tolerant in freezing and thawing processes.
* Syneresis Measurement Method: Insert filter paper (width 1 cm × length 11 cm) into the prepared gel (insert 1 cm at the tip) and measure the syneresis distance (cm) shown on the filter paper after 1 hour. The shorter the distance (= less water separation), the better the water retention capacity is.
-
- Syneresis of pea protein gel
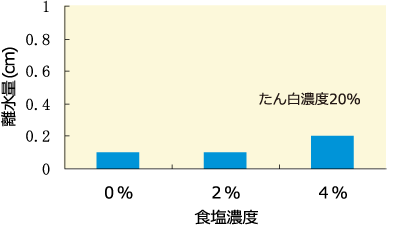
- The result of making pea protein according to gel forming property (3.5 times added water, heated in boiling water for 30 minutes)” defined in Japan Agriculture Standard “Plant protein and seasoning vegetable protein” and measuring syneresis (drip) generated from the gel.
-
- Syneresis after frozen and thawed.
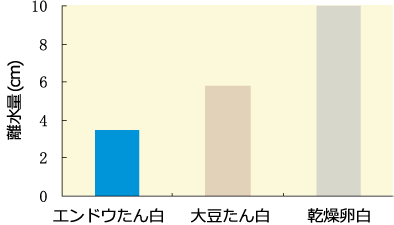
- The result of syneresis of 20% aqueous dispersion of each protein was pressurized and heat-sterilized (retort sterilized) after freeze-thawing treatment.
-
■Heating condition: 120℃. × 20 minutes
■ Freezing condition: -30℃. × 16 hours
■ Thawing condition: 20℃. × 3 hours
Excellent nutritional value
Analysis of Amino Acid Composition of Pea Protein As you can see from the example, the content of lysine, one of essential amino acids, is higher than that of soy protein and wheat protein. (* In the table is an essential amino acid.) It is possible to utilize it as a protein reinforcement material such as health foods and diet foods by making full use of its characteristics.
- Pea protein amino acid composition (g / 100g protein)
-
- Glycine
- 4.6
- Phenylalanine
- 6.1
- Alanine
- 5.0
- Tryptophan
- 1.1
- Valine
- 5.3
- Proline
- 5.3
- Leucine
- 8.4
- Methionine
- 1.3
- Isoleucine
- 5.6
- Cysteine
- 0.8
- Serine
- 4.8
- Lysine
- 6.8
- Threonine
- 4.3
- Histidine
- 2.5
- Tyrosine
- 3.1
- Arginine
- 8.7
- Aspartic acid
- 12.4
- Glutamic acid
- 13.7
- Created (revised) December 2010
















